To Infinity and Beyond!
- Dr. Orna

- Dec 20, 2021
- 5 min read

Folded origami-style inside its rocket cocoon, the James Webb Space Telescope is patiently waiting. While people around the world are getting ready for the holidays, the scientific community is holding its breath and crossing its fingers in anticipation for an astronomic (pun intended) event. On December 24th, very early in the morning (US time), the new space telescope is scheduled to be launched into space from French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope developed by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). It is the most complex and powerful space telescope ever built. It took 20 years to build it, and it is finally ready!
CLICK TO JOIN THE COUNTDOWN
From left to right :
The James Webb Space Telescope, the premier space science observatory of the next decade, is targeted for launch Dec. 24 from Europe's Spaceport in French Guiana, on the northeastern coast of South America. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn
On Saturday, Dec. 11, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope was secured on top of the Ariane 5 rocket that will launch it to space from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana. Credit: ESA-M.Pedoussaut
Engineers posed by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope shortly after it emerged from Chamber A at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston on Dec. 1, 2017. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn
What is a telescope?
A telescope is an instrument that allows people to see far away objects. Telescopes are very important tools in Astronomy that are usually used to view and study planets and stars.
Galileo used a telescope about 400 years ago to make his discoveries. He saw the four large moons around the planet Jupiter, learned that the moon has craters, saw sunspots, and more!
In the late 1600s, Isaac Newton used mirrors instead of lenses to develop the reflecting telescope.
From left to right - Galileo Galilei, Newton's telescope, Isaac Newton (Wikipedia).
To learn more about how telescopes work see HERE.
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST)
The Hubble Space Telescope is the most famous space observatory ever flown. It is named after Edwin Hubble (1889–1953) - a pioneer of modern astronomy.
The Hubble is powered by solar panels and was designed in a way that astronauts would be able to fix problems or replace old instruments.
This 11 ton telescope was placed in an orbit 350 miles high around Earth in April,1990. it completes a full circle around Earth every 96 minutes, and so far it has traveled more than 5 billion miles! Since it is located outside Earth's atmosphere, the Hubble has a good view of outer space without any background light; during its 30 years of work, it took amazing pictures of far away stars and galaxies.
From left to right: The Hubble Space Telescope; Edwin Hubble; Hubble Captures the Shredded Remains of a Cosmic Explosion. (NASA)
The James Webb Space Telescope
(AKA JWST or simply the Webb)
The James Webb Space Telescope that is planned to be launched on Friday December 24 is predicted to work for 5-10 years.
How much did it cost?
10 billion USD
How much does it weigh?
14,000 pounds
How big is it?
VERY VERY BIG!!!
The Webb telescope is as tall as a 3-story building and as long as a tennis court! It is so big that it has to be folded to fit inside the rocket to launch. The telescope will unfold (sunshield first) once in space.
How will it be launched?
The Webb will be launched using the Ariane 5 rocket that NASA has already used multiple times to send missions to space. It is a European heavy-lift space launch vehicle developed and operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency.
Where is French Guiana and why is it launching from there?
The Webb will be launched from the Guiana Space Centre in French Guiana. French Guiana is located on the north Atlantic coast of South America.
It is near the equator, so less energy is required to steer a spacecraft into an orbit.
Rockets launch to the east to take advantage of Earth's rotation momentum. French Guiana has open sea to the east, so if a launch fails (or if there is any debris), it is less likely to fall on people or buildings.
From left to right :
French Guiana is on the north Atlantic coast of South America
Ariane 5 Ariane 5 ES with ATV-4 on board on its way to the launch pad in June 2013 (Wikipedia)
The James Webb Space Telescope is about the same size as a tennis court and about as tall as a 3-story building! Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
How far will it go?
While the Hubble is orbiting the Earth 354 miles above us, the Webb destination is almost one million miles away, and will orbit the Sun just like Earth and all the other planets.
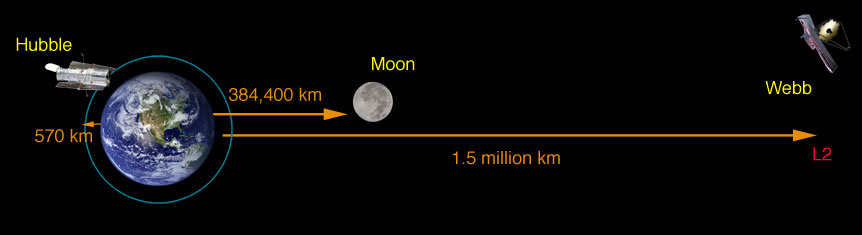
Above - Webb will orbit the sun 1.5 million kilometers (1 million miles) away from the Earth at what is called the second Lagrange point or L2. (Note that these graphics are not to scale.) (NASA)
How long will it take for the Webb to reach its destination?
Timeline:
Cross your fingers - and countdown together for liftoff
206 seconds after liftoff, the fairing that protects the space telescope from the wind and friction of launch will open, exposing Webb to space for the first time.
Shortly after this happens, Webb should send its first communications to operators on the ground.
At 28 minutes after liftoff, Webb will separate from the launch vehicle.
Between 31 and 33 minutes after separation, the telescope’s solar array will extend and begin powering Webb’s systems.
Two days after the launch, the telescope will pass by the Moon.
12 days after launch, the main mirror will begin to unfold, followed by 10 days of opening up all 18 mirrors (this will be done from the control center on Earth).
We are still crossing our fingers - lots of things need to go right in order for the Webb to reach its destination.
The telescope will take 29 days to reach its destination (a million miles from Earth).
5 months of checks and adjustments.
6 months after the launch the Webb will be ready to start studying the universe, collect data adn send pictures! - SO EXCITING!!
More about the the James Webb Space Telescope:
How to watch:
Even if you are not an early riser - consider setting your alarms on Christmas Eve and waking up (super early) to watch the launch live ( https://www.nasa.gov/nasalive)
Dec. 24, Friday (all times are Eastern US time zone) 3 a.m. – Update on the fueling of the Ariane 5 rocket for the James Webb Space Telescope launch from Kourou, French Guiana. 3:15 a.m. – James Webb Space Telescope highlights and launch pad views from Kourou, French Guiana. 4:45 a.m.– Ariane 5 rocket/James Webb Space Telescope launch pad views and James Webb highlights from Kourou, French Guiana. 6 a.m. – Coverage of the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope on an Ariane 5 rocket from the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana (launch scheduled at 7:20 a.m. EST) Goddard Space Flight Center/Space Telescope Science Institute/Kourou, French Guiana. 9 a.m. – Webb Space Telescope post-launch briefing from Kourou, French Guiana (All Channels).
What will happen to the Hubble in the future?
NASA predicts that Hubble will last for many more years, continue its observations, and work together with the Webb.
The James Webb Space Telescope has been designed to explore and answer many questions.
What would you like the Webb to explore?
Please add your answers in the comments below!
Vocabulary
Astronomy - the study of the Universe and everything in it, including planets, stars, galaxies, comets, and black holes. It's full of huge distances, gigantic sizes, and long periods of time.
Telescope - an instrument that uses lenses and sometimes mirrors to make distant objects appear larger.
NASA - United States organization that conducts space travel and research. NASA stands for "National Aeronautics and Space Administration".
Galaxy - A huge collection of gas, dust, and billions of stars and their solar systems, all held together by gravity.




























Comments